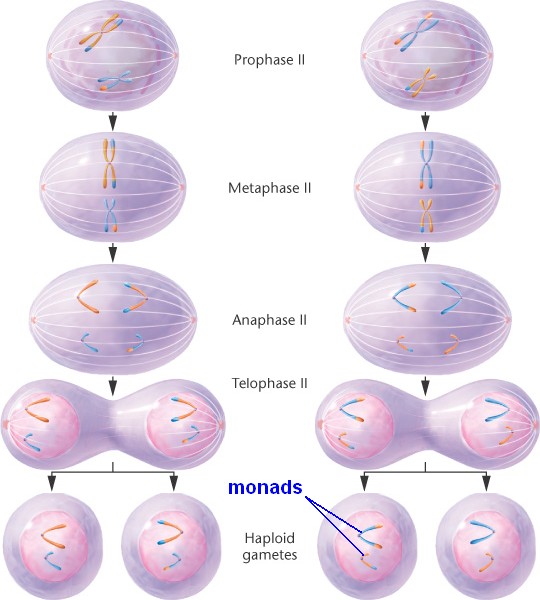
 Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, except the cell undergoing division is
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, except the cell undergoing division is haploid
rather than diploid.
In prophase II,
each dyad has two chromatids attached to a common centromere.
In metaphase II,
chromosomes move to the metaphase plate, and centromeres start to divide.
In anaphase II,
the divided centromeres pull sister chromatids to opposite poles (disjunction).
After telophase II and cytokinesis II,
cell division is complete, producing monads.
Each haploid daughter cell is a potential gamete and has one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes.
Note that if disjunction fails (nondisjunction) in either meiosis I or II,
the gametes will have abnormal numbers of chromosomes.