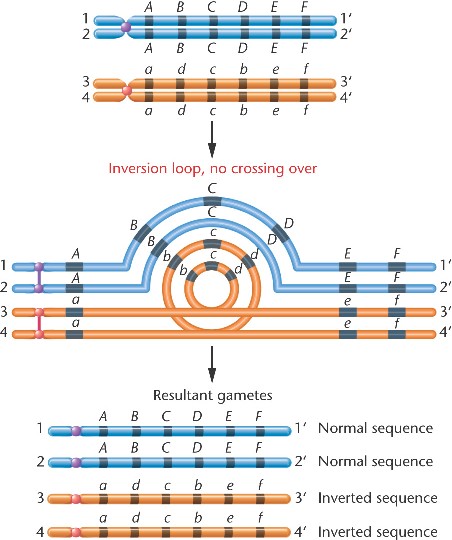
 An inversion heterozygote forms an inversion loop during synapsis.
An inversion heterozygote forms an inversion loop during synapsis.
If crossing over does not occur within the inversion, segregation will produce a 1:1 normal:inverted ratio in the gametes, and 1/2 the offspring will inherit the inversion.
However, if crossing over does occur within the inversion loop,
abnormal
chromatids are
produced,
with reduced gamete viability.
This is likely with large inversions.