T - A pair has mutated to C - G.

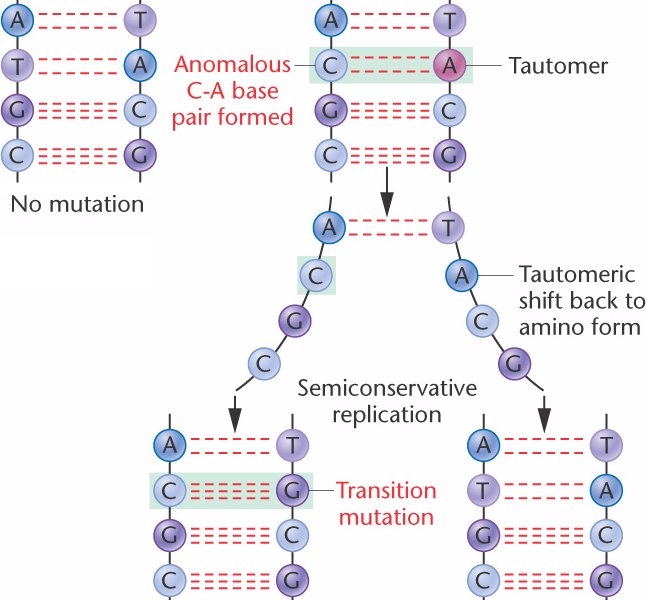 In the next round of replication, the mismatched members of the base pair separate;
the tautomer usually shifts back to its normal isomer.
In the next round of replication, the mismatched members of the base pair separate;
the tautomer usually shifts back to its normal isomer.
Replication of the 2 strands by normal base pairing results in a point mutation called a
transition mutation, where a purine substitutes for a purine,
or a pyrimidine substitutes for a
pyrimidine.
In this example, the wild type T - A pair has mutated to C - G.
