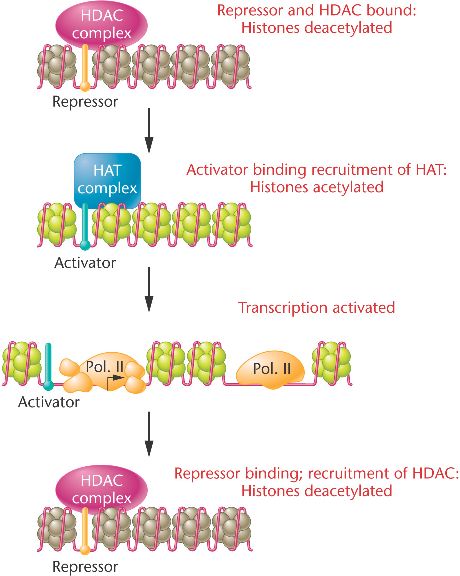
 The enzyme histone acetyltransferase (HAT) catalyzes the addition of
The enzyme histone acetyltransferase (HAT) catalyzes the addition of acetate groups to histone tails,
reducing the attraction between the basic histone protein and acidic DNA, thus opening the chromatin and
activating the gene.
The acetylation can be reversed by
histone deacetylase (HDAC), thus closing the chromatin and repressing the gene.