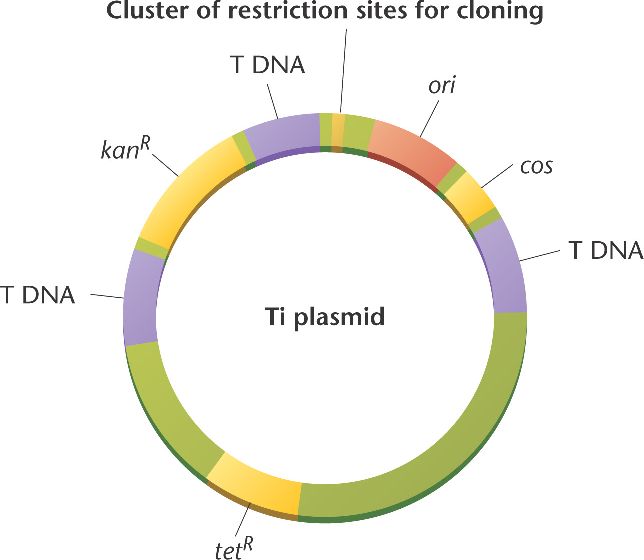
 A tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of the bacterium Agrobacterium tumifaciens
can be used as a vector for DNA cloning in
A tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of the bacterium Agrobacterium tumifaciens
can be used as a vector for DNA cloning in plants.
The plasmid T DNA, necessary for integration, are combined with bacterial DNA that contain an origin of replication (ori), restriction sites and antibiotic resistance genes (KanR and tetR).
When the bacterium infects a plant, the T DNA, together with any cloned DNA, integrates into a host chromosome, producing a transgenic plant.
This process is caled transformation.