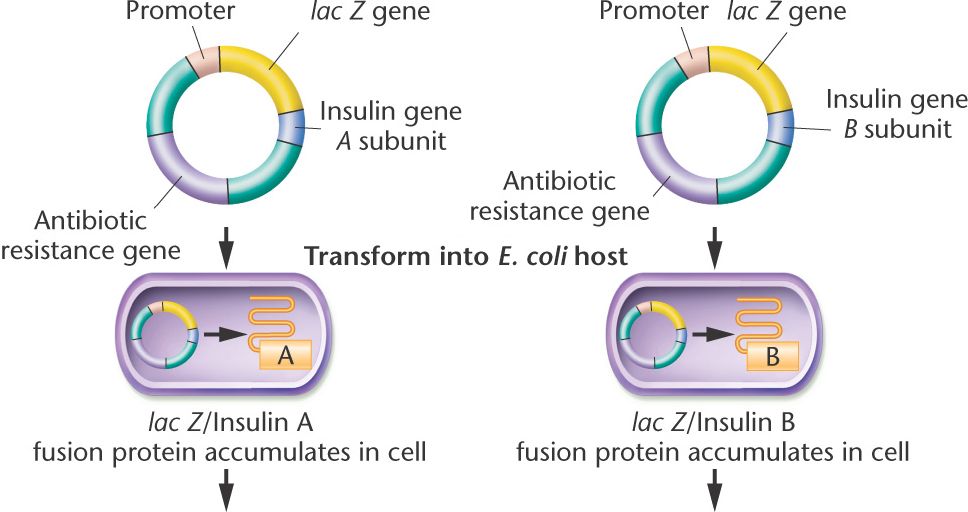
To synthesize recombinant human insulin, synthetic oligonucleotides encoding the
insulin A and B
chains
are inserted into a plasmid together with an an antibiotic resistance gene and
the E. coli lacZ
gene
and its promoter to yield an expression vector.
The recombinant plasmids are transferred to E. coli hosts,
where β-galactosidase/insulin fusion proteins are
produced.
