 Inbreeding among relatives reduces genetic variation by decreasing heterozygote frequency.
Inbreeding among relatives reduces genetic variation by decreasing heterozygote frequency.
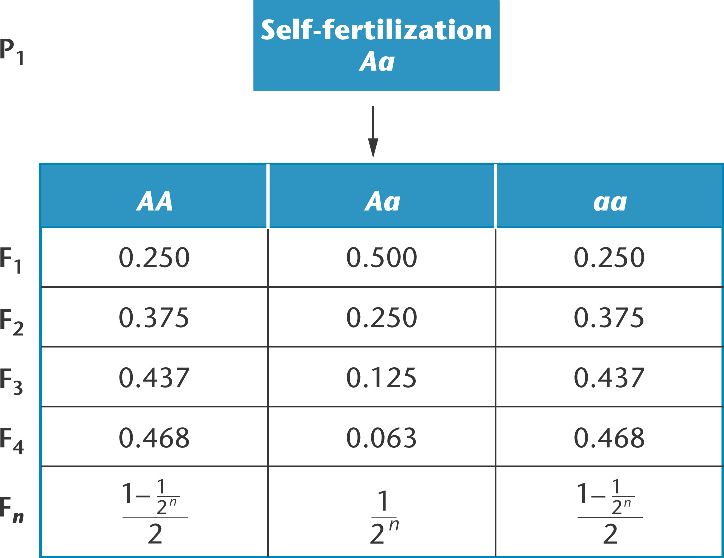
In the extreme form of inbreeding, self-fertilization, for an individual heterozygous at one locus, 94% of its descendants are homozygous in 4 generations.
Note, however, that the allele frequencies of A and a remain unchanged at 50%.